- HOME
- Technology
- Vacuum Deposition
Vacuum Deposition
The Vacuum Deposition process
Vacuum Deposition deposits the following on films: Polyethylene terephthalate (PET),
Polypropylene (PP), Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS), Polyimide (PI), Aramid
It also deposits mainly aluminum, zinc, and copper on metals.
The interior of a Vacuum Deposition machine is divided into a winding chamber and a Vacuum Deposition chamber. Metal is heated in a high vacuum, promoting evaporation. This enables the adherence of the substance on the surface of the plastic film.
A high vacuum means there is pressure surrounding the area that creates an aurora in the space (Height: 100 to 300 km).
A Vacuum Deposition film thickness from 100 Å to 20,000 Å is possible. (10nm to 2,000 nm)
We have three different methods for heating metal to be deposited.
They are:
- High-frequency induction heating method
- Resistance heating
- Electron beam
A margin, or a portion on which there is no Vacuum Deposition, is required for using metallic Vacuum Deposition film as a Capacitor. The function for forming this margin is incorporated in the vacuum Vacuum Deposition machine.
The high-frequency induction heating method
The metal is melted by heating it to approx. 1,400 to 1,500°C in a crucible.
A magnetic field is created by passing a current through the coil, and the crucible is heated.
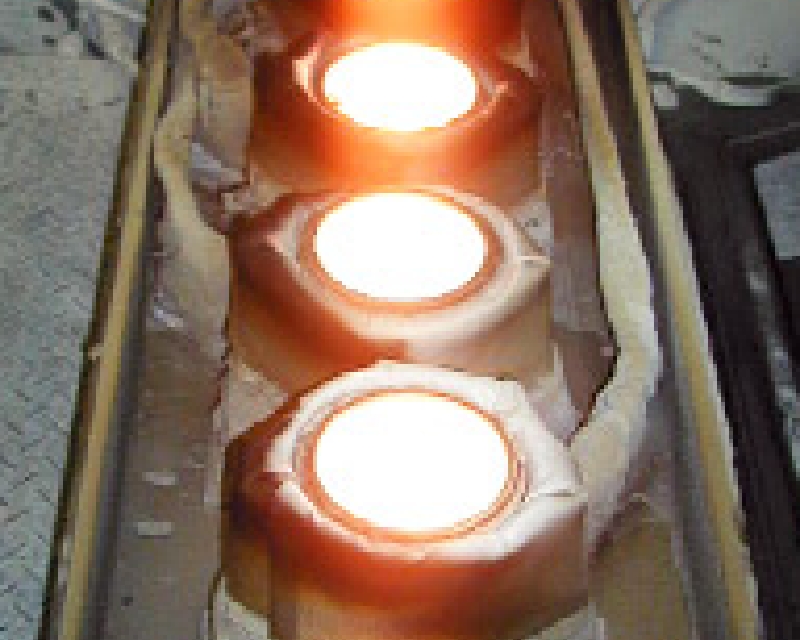


Resistance heating method (Energized heating method)
A boat is heated and aluminum wire is continuously fed into it, resulting in Vacuum
Deposition.
The metal is heated by energizing the BN composite material, which is both corrosion-proof and
conducts electricity.
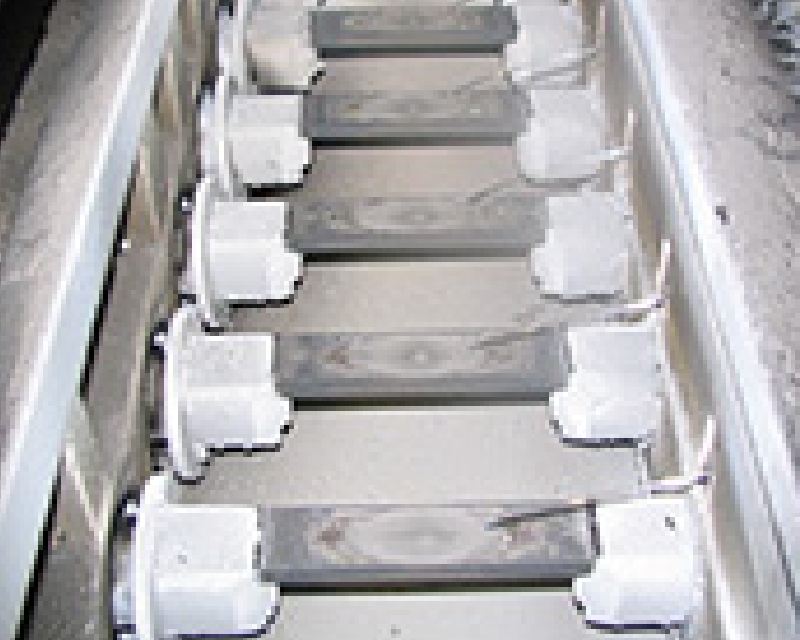


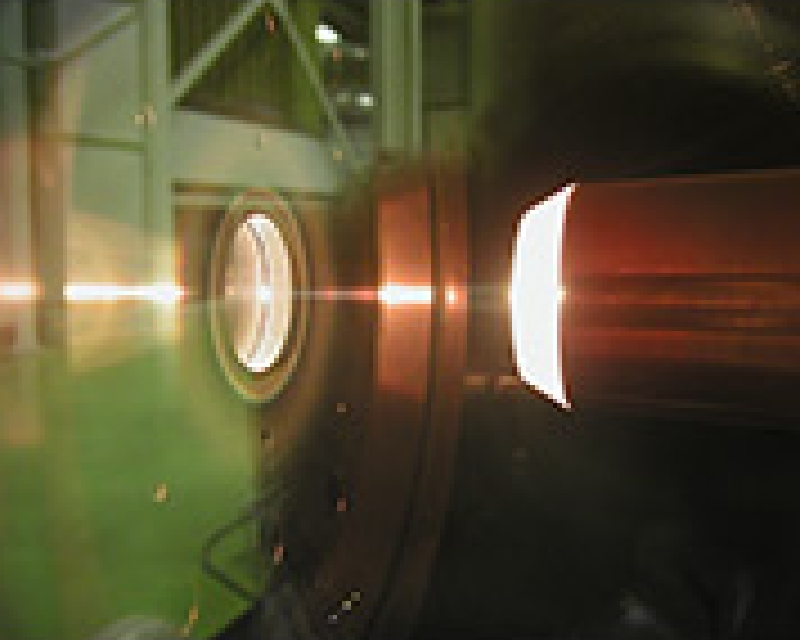
Electron beam method
The metal is heated by focusing an electron beam directly onto the vapor deposit metal. Unlike the other methods, the crucible or the boat is not heated.
Vacuum Deposition machinery
Vacuum exhaust systems of Vacuum Deposition machinery
This achieves the high vacuum ideal for Vacuum Deposition by dividing the exhaust system into three stages.
The high vacuum pump
The pump creates a high vacuum that enables the formation of a uniform Vacuum Deposition layer on the film.
The medium vacuum pump
A relay pump that conveys the action to the high vacuum pump
Roughing vacuum pump
A pump that begins evacuation from the outer air
Vacuum Deposition machinery (Winding type)
The film is fed into the Vacuum Deposition chamber by running it through the flattening roller underneath the CC-1 (cooling roll) from the unwinding side. After the Vacuum Deposition process is finished, the film is cooled and rewound through the flattening roller.
Vacuum Deposition is possible starting from 1 µm of the thinnest film thickness.
Margin process I / Oil margin
- Our expertise resulted in the creation of oil margin technology.
- The process enables a minimum product width of 2.25 mm, with a 0.25 mm margin.
- We use liquid chromatography to measure the adhesion volume.
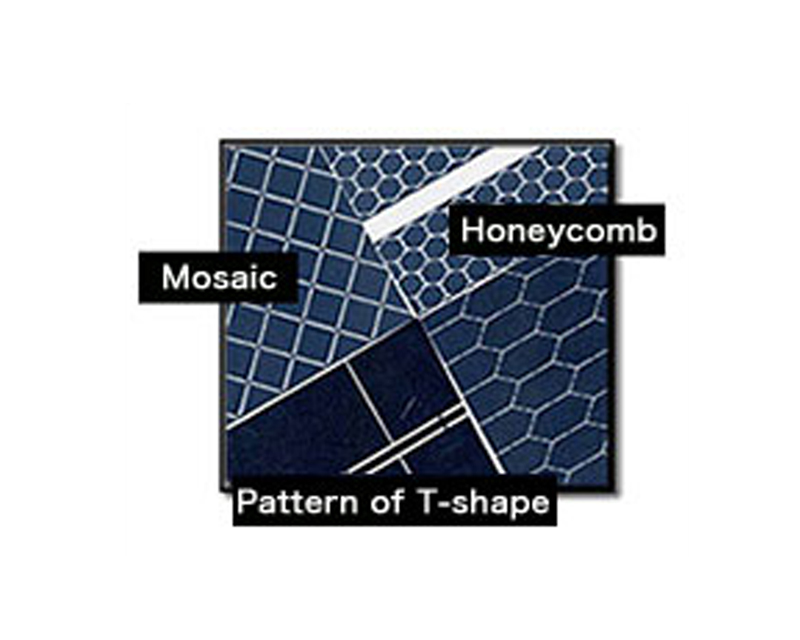
The most advanced pattern technology
- We are capable of handling Vacuum Deposition for all types of patterns to improve safety and electric potential gradient.
- We are now also able to handle more complex and detailed patterns with our improved pattern roll technology.